Bonding process
What is AMALPHA?
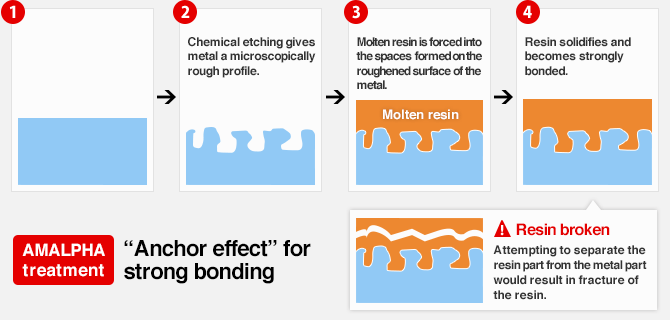
AMALPHA achieves bonding by forcing resin into the microscopically rough surfaces of metal and allowing it to solidify, resulting in what is known as the “anchor effect.”
- Molten resin comes into contact with metal surfaces.
- Molten resin is forced into the microscopically rough surfaces.
- The resin solidifies in the microscopically rough surfaces.
This is the sequence through which AMALPHA bonding is completed.
AMALPHA bonding mechanism
AMALPHA: resin-to-metal bonding technology
Since the resin is embedded in microscopically roughened metal surfaces and solidifies, attempts to separate the resin from the metal with force would result in fracture of the resin part, which is a base material fracture.

Cu-phenol
x3000 1μmAfter being forced into a microscopically rough metal surface, resin solidifies.
Resin molding method
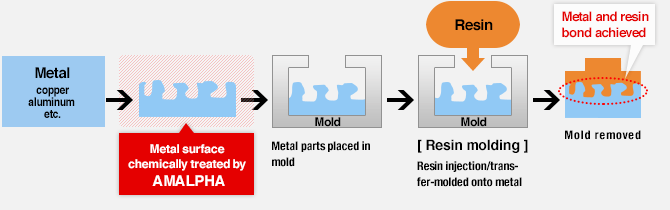
All kinds of molding method can be used to achieve resin-to-metal bonding if molten resin is allowed to come into contact with a metal surface under sufficient pressure.
Example resin molding method
| Molding method | Description |
|---|---|
| ・Insert injection molding ・Transfer molding |
Metal parts are inserted in a mold. Then molten resin is injected into the mold. |
| ・Heat pressing | Metal and thermal plastic resin surfaces are joined and subjected to heat and pressure. |
| ・Painting ・Coating |
After being applied onto a metal surface, fluid resin is allowed to solidify. |
| ・Laser welding | Metal and resin surfaces are joined. Then the metal is heated by laser beams to melt the thermal plastic resin. |