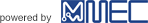Performance
Performance/Control
MEC uses the following test methods to examine AMALPHA bonding conditions.
- Compressive shear strength test
- Vertical tensile strength test
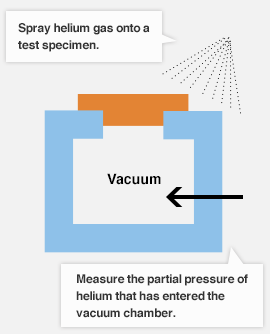
- Airtightness test (helium leak/underwater airtightness)
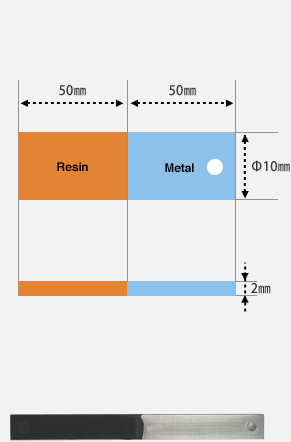
Test specimen geometry
Test specimen for compressive shear/airtightness test
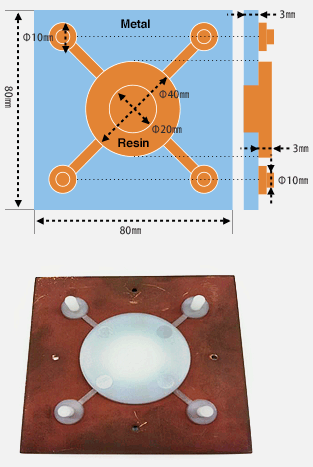
Test specimen for tensile/compressive shear test
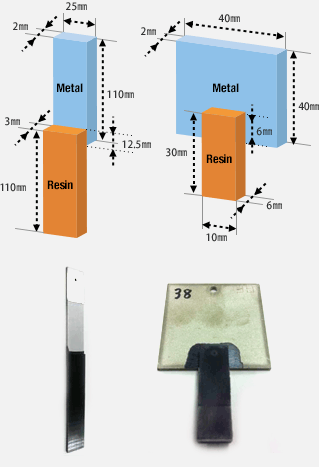
Test specimen for airtightness test
Test specimen for tensile test
Measuring apparatuses

Autograph
(bonding strength measurement)

Helium leak tester

Thermal cycle tester

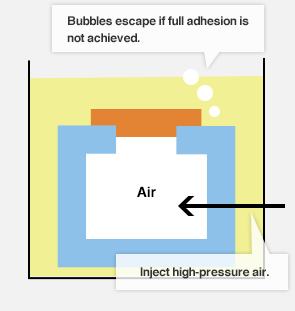
Jigs for underwater airtightness test
Measurement methods
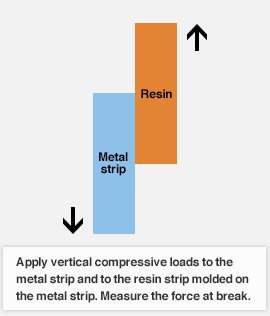
Compressive shear strength
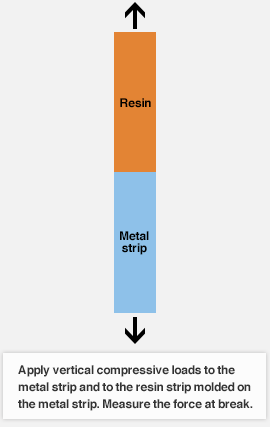
Tensile shear strength
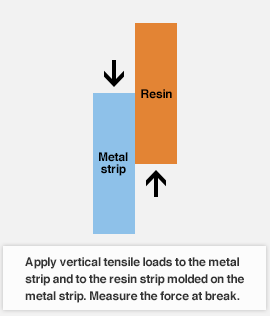
Vertical tensile strength
Helium leak test
Jigs for underwater airtightness test
Results of strength test (compressive shear)
| Metal | Resin | Bonding strength |
|---|---|---|
| A5052 | PPS | 41.7MPa |
| C1100 | PPS | 36.8MPa |
| SUS304 | PPS | 40.9MPa |
Results of airtightness test (helium leak)
| Al | SUS | Cu | |
|---|---|---|---|
| PPS | ○ | ○ | ○ |
| PA6 | ○ | ○ | ○ |
| PA66 | ○ | ○ | ○ |
| Phenol | ○ | ○ | ○ |
| Epoxy | ○ | ○ | ○ |
- ○:1.0 x 10-10 Pa∙m3/s max. in helium leak test (lower than leak detection limit)
In all of these tests, test specimens failed due to fracture of resin. In practice, these tests measured the strength of the resin. The true resin-to-metal bonding strength is presumed to be higher than the values shown above. In addition, results of tensile strength tests would be approximately 30 MPa since the resin would break somewhere in its middle portion.
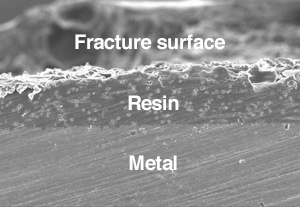
SEM image of fracture surface of resin
x100 100μmThe resin-to-metal bonding interface of failed test specimens monitored using SEM reveals that the bonding is intact at the interface.